 :
: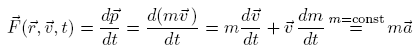 :
:Newton's 3rd law is given by:
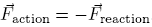
For the power P holds:
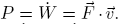 . For the total energy W, the kinetic energy T and the potential energy U holds:
. For the total energy W, the kinetic energy T and the potential energy U holds: 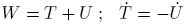 with
with 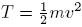 .
.The kick
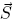 is given by:
is given by: 
The work A, delivered by a force, is

The torque
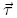 is related to the angular momentum
is related to the angular momentum 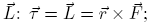 and
and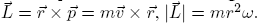 . The following equation is valid:
. The following equation is valid:
Hence, the conditions for a mechanical equilibrium are:
 .
.The force of friction is usually proportional to the force perpendicular to the surface, except when the motion starts, when a threshold has to be overcome:
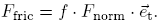 .
.Conservative force fields
A conservative force can be written as the gradient of a potential: . From this follows that
. From this follows that  . For such a force field also holds:
. For such a force field also holds: 
So the work delivered by a conservative force field depends not on the trajectory covered but only on the starting and ending points of the motion.
Gravitation
The Newtonian law of gravitation is (in GRT one also uses K instead of G):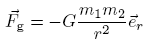
The gravitational potential is then given by
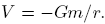 . From Gauss law it then follows:
. From Gauss law it then follows: 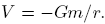 .
.Orbital equations
If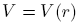 one can derive from the equations of Lagrange for
one can derive from the equations of Lagrange for  the conservation of angular momentum:
the conservation of angular momentum:
For the radial position as a function of time can be found that:

The angular equation is then:

If
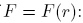 L =constant, if F is conservative: W =constant, if
L =constant, if F is conservative: W =constant, if 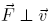 then
then  and
and  .
.Kepler's orbital equations
In a force field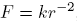 , the orbits are conic sections with the origin of the force in one of the foci (Kepler's 1st law). The equation of the orbit is:
, the orbits are conic sections with the origin of the force in one of the foci (Kepler's 1st law). The equation of the orbit is:
with

a is half the length of the long axis of the elliptical orbit in case the orbit is closed. Half the length of the short axis is
 is the excentricity of the orbit. Orbits with an equal
is the excentricity of the orbit. Orbits with an equal  are of equal shape. Now, 5 types of orbits are possible:
are of equal shape. Now, 5 types of orbits are possible:1. k < 0 and= 0: a circle.
2. k < 0 and 0 << 1: an ellipse.
3. k < 0 and= 1: a parabole.
4. k < 0 and> 1: a hyperbole, curved towards the centre of force.
5. k > 0 and> 1: a hyperbole, curved away from the centre of force.
Other combinations are not possible: the total energy in a repulsive force field is always positive so
 .
.If the surface between the orbit covered between
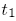 and
and 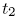 and the focus C around which the planet moves is
and the focus C around which the planet moves is 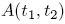 , Kepler's 2nd law is
, Kepler's 2nd law is
Kepler's 3rd law is, with T the period and
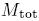 the total mass of the system:
the total mass of the system: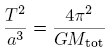
The virial theorem
The virial theorem for one particle is:
The virial theorem for a collection of particles is:

These propositions can also be written as:
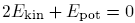 .
.