Operations and Expressions
FORTRAN provide five basic arithmetic operations: Addition +
Subtraction -
Multiplication *
Division /
Exponentiation **
|
FORTRAN expressions| Mathematical Notation | Correct Expression | Incorrect Expression |
|---|
| a.b | A*B | AB (no operation) | | a.(-b) | A * (-B) or -A*B | A*-B (two operations side by side) | | a+2 | A+2.0 | A=2 (mixed integer and real) | | -(a+b) | -(A+B) or -A-B | -A+B or -+A+B | | {a+[b.(c-d)-c]+b} | A+(B*(C-D)-C)+B) | {A+[B*(C-D)-C]+B} | 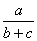 | A / (B+C) | A / B + C | 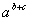 | A ** (B+C) | A ** B + C | 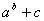 | (A ** B) + C | A ** (B + C) | | | | Lists some examples of correct and incorrect ways of forming FORTRAN expressions. | |
Mathematical Functions
Fortran provides for the use of certain common mathematical functions. |
Mathematical Functions| Mathematical Function | FORTRAN Name |
|---|
| Exponential | EXP | | Natural Logarithm | ALOG | | Common logarithm | ALOG10 | | Sine of an angle in radians | SIN | | Cosine of an angle in radians | COS | | Hyperbolic tangent | TANH | | Square root | SQRT | | Arctangent: Angle computed in radians | ATAN | | Absolute value | ABS | |
|
Arithmetic Assignment Statements
The most important is computing a new value of a variable, which is done with an arithmetic assignment statement. Its general form is a = b, in which "a" is a variable name, written without a sign, and "b" is any expression.
Examples:
I=10
ABC=12.34
D=2.0
Y=D/5.0
TAN=SIN(D)/COS(D)
ABSVAL=ABS(TAN)
|